In a bold stride toward bridging India’s long-standing rural healthcare gap, artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a life-saving force, turning everyday smartphones into diagnostic devices. As millions in rural India continue to face steep barriers to accessing specialized medical care, AI is becoming a transformative tool, bringing specialist-level insights directly into the hands of local health workers.
While cities boast world-class hospitals and advanced treatments, rural India—home to almost 70% of the population—remains severely underserved. According to government reports, less than 30% of India’s doctors serve in these regions, resulting in delayed diagnoses, worsening chronic conditions, and preventable fatalities.
But a silent revolution is underway, one powered not by brick-and-mortar hospitals, but by mobile technology and smart algorithms.
Empowering Health Workers: The First Line of AI Defense
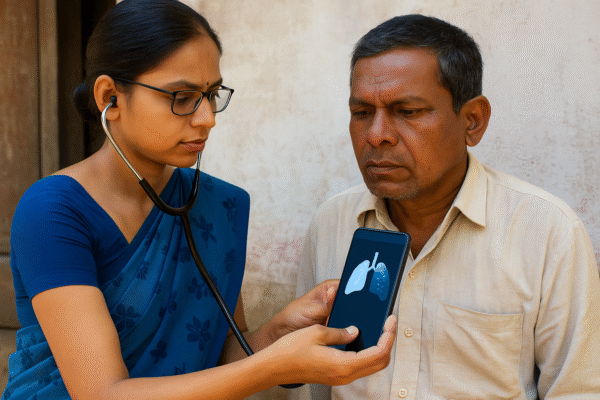
Rather than relying solely on building expensive infrastructure, India is empowering its existing network of Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) and other community health workers. These frontline workers, already trusted within their communities, are now being trained to use AI-based mobile tools for primary screenings.
Equipped with smartphones or tablets, they can screen patients using apps that detect early signs of common diseases. These tools are built to be intuitive and multilingual, ensuring accessibility regardless of the user’s literacy level.
One such program, known as “AI Vaidya,” has been piloted across multiple states and is rapidly expanding. Developed in collaboration with public health experts and AI researchers, it integrates tools that detect anomalies in breathing patterns, eye conditions, and more—with remarkable accuracy.
Smartphones Turned Medical Devices
Imagine a rural health worker using a ₹1,000 lens attachment to transform a phone camera into a retinal scanner. With a single image, the AI can detect signs of diabetic retinopathy, potentially preventing blindness.
Similarly, mobile microphones can be transformed into digital stethoscopes. AI algorithms analyze respiratory sounds to flag illnesses like tuberculosis and pneumonia. These aren’t final diagnoses—but effective screening tools that help health workers identify high-risk patients for further treatment.
By using these AI-enhanced tools, rural residents avoid unnecessary travel, saving both time and money. They no longer need to gamble on a costly hospital visit without knowing whether it’s truly necessary.
Economic Relief and Health Equity
The economic burden of healthcare is especially acute in rural areas. A trip to a city hospital can involve multiple days of lost wages, travel expenses, and consultation fees—sometimes costing families an entire month’s income.
AI health tools offer a cost-effective alternative. With early diagnosis and remote screening, only those who genuinely need advanced care are referred to city hospitals. Chronic illnesses like diabetes or hypertension, when caught early, are far cheaper to manage and treat locally.
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare notes that integrating digital health tools has improved patient compliance and led to earlier treatment in remote districts across Bihar, Jharkhand, and Odisha.
Tackling Barriers: Trust, Training & Connectivity
Despite its promise, deploying AI in rural healthcare isn’t without hurdles.
First, there’s trust. In many villages, residents are more comfortable with human interaction than machine predictions. Here, community health workers play a crucial role—acting as both caregivers and tech interpreters, building confidence in the new system.
Second, training is essential. Even intuitive apps need proper onboarding. Government initiatives and NGOs are conducting training sessions to ensure that health workers understand both the capabilities and the limitations of AI tools.
Third, connectivity remains a major challenge. Many areas lack reliable internet. Developers have solved this by building AI apps that work offline. Data is stored locally and synced when connectivity returns, ensuring functionality in even the remotest villages.
A Vision for the Future
India’s AI-driven rural healthcare model is not a futuristic vision—it’s happening now. States like Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and Telangana are integrating AI into public health missions, often in partnership with research labs and health tech startups.
The goal is not to replace doctors but to amplify the reach of existing healthcare systems, reduce the diagnostic burden, and bring equity into the healthcare narrative.
The future of Indian healthcare isn’t just in hospitals—it’s in handheld devices powered by intelligence, guided by empathy, and delivered by people who live among those they serve.
In a country as vast and diverse as India, AI might just be the bridge that connects the promise of modern medicine with the people who need it most.
For more travel news like this, keep reading Global Travel Wire