U.S. Immigration Enters a New Surveillance Era
Washington D.C. – The U.S. immigration system is undergoing one of its most significant transformations in decades, introducing advanced biometric screenings and continuous monitoring that will reshape how millions interact with the process of entering and staying in the country. This shift reflects a broader move toward surveillance-driven enforcement, with far-reaching effects for travelers, students, and professionals.
Biometric Expansion at an Unprecedented Scale
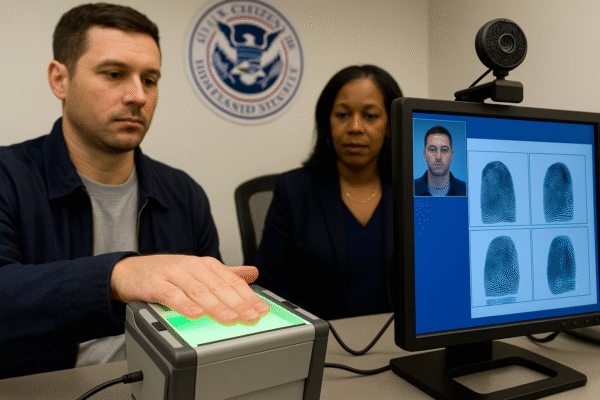
The U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) is spearheading a sweeping expansion of biometric data collection. Under this initiative, annual biometric submissions are expected to grow from roughly four million to over six million—a surge exceeding 60 percent.
This expansion moves far beyond traditional fingerprinting. New requirements will include iris scans, palm prints, voice samples, and in some cases, even DNA analysis. The scope of this initiative underscores the government’s push to tighten identity verification and minimize fraud in the immigration process.
For applicants, this means that legal entry into the United States will involve a more complex and intrusive process, creating additional hurdles for those navigating work, student, or family-based immigration pathways.
Continuous Vetting: A New Standard
Perhaps the most dramatic change is the implementation of “continuous immigration vetting.” This system does not stop once an applicant enters the country. Instead, noncitizens will remain under ongoing monitoring, with their records checked against law enforcement and intelligence databases throughout their stay.
This constant screening means visa holders—whether tourists, students, or employees—could have their status re-evaluated at any time. Advocates argue this enhances national security by swiftly identifying threats, but critics contend it raises serious privacy concerns and risks creating an environment of perpetual surveillance.
Reviving the Alien Registration System
In tandem with biometric expansion, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has reinstated the long-dormant Alien Registration Biographic Information requirement, also known as Form G-325R.
This regulation mandates that most noncitizens aged 14 and older register with the government if they remain in the U.S. for more than 30 days. The registration process collects detailed biographical information, including addresses, employment history, and biometric identifiers such as fingerprints and photographs.
Once processed, individuals over 18 are required to carry proof of registration at all times. This policy ensures that even those with limited interaction with immigration authorities are now fully documented and traceable.
Stricter Rules for Visa Programs
Alongside these surveillance measures, the U.S. government is tightening visa requirements, including the Diversity Visa (DV) lottery program. Applicants must now possess a valid passport and provide full passport details at the time of application.
This change, which mirrors a previous short-lived policy, is expected to significantly reduce participation from lower-income countries, particularly in Africa and Asia, where access to passports is limited. Critics argue that these rules undermine the original purpose of the Diversity Visa program by reducing representation from underrepresented regions.
Impacts on Travel, Education, and Workforce
Industry experts warn that the heightened surveillance, stricter requirements, and additional costs could deter international students, skilled workers, and tourists from considering the U.S. as a destination.
Educational institutions are voicing concerns that unpredictable visa durations and increased scrutiny will push international students toward countries with more stable and transparent systems. Similarly, employers—especially in sectors like healthcare and technology—fear these measures could exacerbate talent shortages, as foreign professionals may opt for nations with less complex immigration pathways.
Privacy and Civil Liberties Concerns
Civil liberties groups have raised alarms over the growing scope of biometric collection and continuous vetting. Once collected, biometric data could be shared across multiple government agencies and international databases with limited transparency or oversight.
Advocates caution that such extensive data collection poses risks of misuse, potential hacking, and erosion of privacy for both noncitizens and U.S. citizens subject to certain data collection requirements.
Furthermore, the integration of social media monitoring into the vetting process has sparked debate over freedom of speech. Some travelers and students have already reported visa revocations linked to online posts flagged by automated systems.
Looking Ahead: A New Immigration Landscape
While some of these changes are still in the regulatory review and public comment stages, others have already taken effect, signaling a clear trajectory for the future of U.S. immigration.
Legal immigration is steadily shifting from a service-focused framework to one dominated by surveillance, higher costs, and tighter control. For millions of people worldwide, the path to entering and remaining in the United States is becoming more complex, more expensive, and far more monitored than ever before.
As the reforms continue to roll out, travelers, students, and professionals navigating the immigration system will need to adapt to this new reality—one where technology, security, and continuous oversight define every step of the journey.
For more travel news like this, keep reading Global Travel Wire