The United States is leading a transformative leap in air travel security with the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) deploying artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced automation at airport checkpoints. In an ambitious push to modernize U.S. airport infrastructure, the TSA’s AI-powered security enhancements aim to shorten wait times, increase detection accuracy, and improve the overall passenger experience across the country.
Why AI Now? Responding to Skyrocketing Passenger Volumes
With domestic and international air travel volumes rebounding to pre-pandemic levels and surpassing 2.9 million passengers daily during peak periods, U.S. airports have faced mounting pressure on outdated security systems. According to the U.S. Department of Transportation, increasing traveler throughput without compromising safety is now a critical challenge.
The TSA’s adoption of AI-driven solutions is a direct response to this urgent need. The agency has partnered with private sector tech firms and federal research labs to develop screening systems that reduce bottlenecks while improving accuracy. This move aligns with broader goals under the Biden Administration’s Blueprint for a 21st Century Aviation Security System, which prioritizes technology-forward initiatives.
How AI and Robotics Are Transforming TSA Checkpoints
The TSA’s smart screening transformation revolves around three core technologies:
- AI-based threat detection systems
- Robotic screening assistants
- Automated carry-on and checked luggage scanning
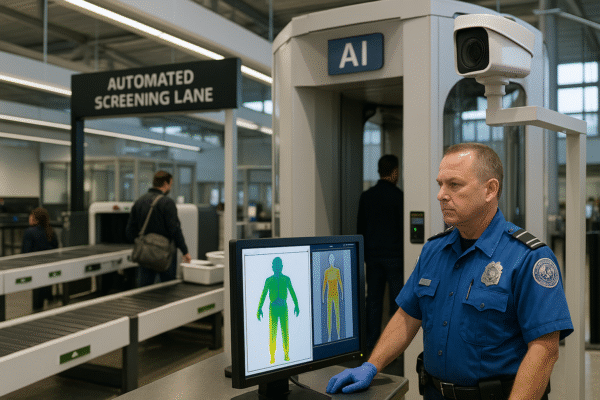
AI algorithms trained on millions of X-ray and CT scan images are being implemented to detect prohibited items in real time with higher precision than human screeners. These systems can instantly flag potential threats, minimizing human error and enabling secondary checks only when necessary.
Additionally, robotics are being deployed to assist with repetitive tasks like tray management and guiding passengers through biometric checkpoints. TSA agents, instead of monitoring each individual scan, are now tasked with supervisory roles—making decisions based on AI recommendations and managing exceptions.
In pilot programs at major airports including Atlanta Hartsfield-Jackson (ATL), Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), and John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK), automated screening lanes equipped with smart trays and dynamic lighting systems have already demonstrated a 30–40% reduction in passenger processing times, according to TSA officials.
Benefits for Passengers: Speed, Security, and Simplicity
The most immediate impact for travelers will be significantly reduced wait times. Long queues at checkpoints—once a dreaded part of airport travel—are expected to shrink as automated systems expedite bag checks and biometric identity verification. Travelers enrolled in TSA PreCheck and CLEAR will also benefit from seamless integration with AI-powered lanes.
More importantly, security outcomes are expected to improve. AI can identify concealed weapons, liquid explosives, and non-metallic threats far more effectively than traditional systems, ensuring higher passenger safety while reducing false alarms and unnecessary bag checks.
Addressing Privacy and Employment Concerns
With increased use of biometric data and facial recognition technologies, privacy advocates have expressed concerns over passenger data handling. The TSA has clarified that biometric images are encrypted, stored temporarily, and never shared with external agencies unless legally required. All systems are governed by DHS Privacy Impact Assessments, with oversight from the Department of Homeland Security’s Office for Civil Rights and Civil Liberties.
On the employment front, TSA Administrator David Pekoske emphasized that “AI is not replacing humans—it’s augmenting them.” Far from eliminating jobs, the agency plans to retrain TSA officers for analytical, technical, and decision-making roles as part of the transition. New AI-integrated systems will require human oversight and intervention, particularly in emergency or ambiguous scenarios.
Timeline and Future Deployment Plans
The TSA’s technology rollout is already underway, with expanded deployments expected through 2026. Major hubs including Chicago O’Hare (ORD), Dallas-Fort Worth (DFW), and Denver International Airport (DEN) are scheduled to receive next-generation screening systems within the next 12–18 months.
In line with the Federal Aviation Administration Reauthorization Act of 2024, funding for AI-driven security enhancements has been secured through a combination of federal grants and public-private partnerships.
Looking Ahead: A Smarter, Seamless Travel Experience
The TSA’s AI initiative is more than just a tech upgrade—it marks a fundamental shift in how the U.S. approaches airport security. With enhanced data analytics, predictive screening, and human-machine collaboration, the new system offers a blueprint for next-generation travel that balances safety, efficiency, and passenger convenience.
Moreover, these innovations may serve as a model for other countries. The U.S. is already in talks with international aviation regulators and airport authorities in Europe and Asia to share AI-based threat detection protocols, potentially ushering in a new global standard.
As the TSA continues to invest in smarter tools and scalable solutions, U.S. travelers can expect airport visits to become less stressful, more predictable, and infinitely more secure—a welcome development in an era of rising demand and global mobility.
For more travel news like this, keep reading Global Travel Wire