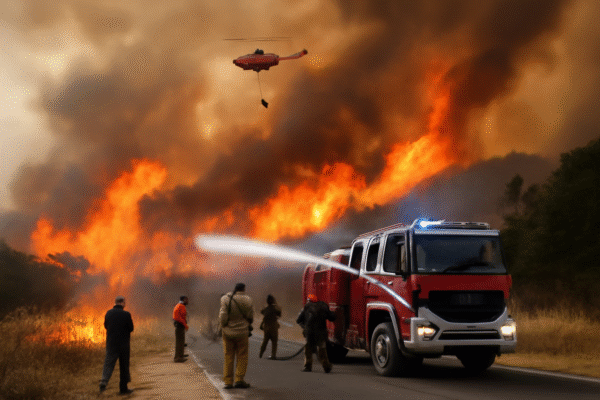
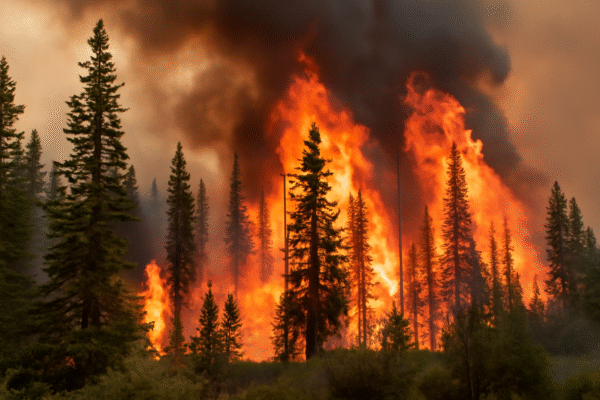
Canada is facing one of its worst wildfire seasons in recent memory, with the 2025 fires causing widespread destruction, health risks, and environmental devastation. As of August 2025, over 725 wildfires are active, burning across several provinces, including Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta. The fires, fueled by unusually dry conditions and extreme temperatures, are having a catastrophic impact not only on the Canadian landscape but also on the health of residents and neighboring regions, especially the United States. The thick smoke from these wildfires has already reached parts of the U.S., raising alarms about the health risks posed by prolonged exposure to wildfire smoke.
Wildfire Hotspots Across Canada
Canada is home to vast forests, many of which are now at the mercy of intense wildfires. The wildfire crisis has been particularly severe in provinces like Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Newfoundland. Manitoba, which declared a state of emergency for the second time this year, has seen over 4.3 million acres burned. Saskatchewan has been hit even harder, with the northern part of the province enduring the largest burn area in Canada, totaling an alarming 6.7 million acres. As a result, nearly 3,200 residents from rural and Indigenous communities in Saskatchewan have been evacuated.
Alberta and British Columbia, which were the epicenters of record-breaking wildfires in previous years, are witnessing fewer fires in 2025, but the situation remains critical. Several communities in these provinces are still under evacuation orders, and many areas are at high risk. Newfoundland, typically less prone to such devastating fires, is also facing an escalating situation, with the government deploying armed forces and the Coast Guard to assist in firefighting efforts. Approximately 900 people have been forced to evacuate from the region due to rapidly advancing wildfires.
While Quebec has seen fewer fires this year, the province has not escaped the effects of the disaster. The smoke from Quebec’s wildfires has drifted southward, affecting parts of the U.S. The fires in Quebec, primarily triggered by human activities, have prompted the provincial government to ramp up awareness campaigns on fire prevention and public safety.
The Health Impact of Wildfire Smoke
The widespread smoke from wildfires is causing a public health crisis, not just in Canada, but across the border in the U.S. Wildfire smoke contains harmful particles, particularly PM 2.5, which can penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream, causing respiratory issues such as bronchitis and asthma exacerbation. Health authorities are warning vulnerable populations—children, the elderly, pregnant individuals, and those with pre-existing conditions like heart and lung diseases—against exposure to the hazardous air quality.
In areas severely affected by the smoke, air quality warnings have been issued, advising residents to stay indoors and limit physical activity. The Air Quality Index (AQI) has become a crucial tool for people to gauge the air quality in real time. For those needing to go outside, wearing N95 masks has been recommended as a protective measure against harmful particulate matter.
Climate Change and Its Role in the Wildfire Crisis
The increasing frequency and severity of wildfires in Canada are being exacerbated by climate change. Experts warn that the warming climate, characterized by prolonged dry spells and higher-than-usual temperatures, is creating perfect conditions for fires to spread uncontrollably. The rising global temperatures have made forests more vulnerable to fires, with dry vegetation providing an ideal fuel source.
Michael Waddington, a professor at McMaster University in Ontario, has described the situation as a “tinderbox” for wildfires. The increasing intensity of these fires is directly linked to climate change, which has altered weather patterns and exacerbated the fire season. In addition to natural factors, human-driven environmental degradation and poor forest management practices have further aggravated the situation.
Impact on the United States
The consequences of Canada’s wildfires are not confined to its borders. The thick smoke has traveled across the U.S., affecting air quality in states like Minnesota and North Dakota. This transboundary air pollution has raised concerns about the health of U.S. residents, with many areas issuing air quality warnings and advising citizens to take necessary precautions.
Both Canada and the United States have responded to the crisis by strengthening their cooperation. The Canadian government has worked closely with U.S. authorities, sharing firefighting resources and coordinating efforts to minimize the damage caused by the fires. This joint effort is part of a broader international approach to combat the ongoing environmental crisis.
Future Solutions and International Cooperation
The worsening wildfire season underscores the need for better forest management and more robust firefighting infrastructure. Experts recommend strategies such as controlled burns and forest thinning to reduce the severity of future fires. However, many of the areas affected by wildfires are remote, making it difficult to implement such measures.
Looking forward, governments must focus on long-term solutions that address the root causes of these fires, including improving forest management practices, investing in firefighting technology, and promoting better land-use policies. At the international level, nations need to take more decisive action to combat climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing stricter environmental policies.
The Urgent Need for Global Action
As wildfires continue to ravage forests and cities across Canada, it is clear that the crisis is not just a local issue but a global one. The growing frequency and intensity of wildfires are a clear reminder of the devastating effects of climate change. It is imperative that nations come together to address the underlying issues that fuel such disasters. Governments, both in Canada and globally, must prioritize climate change mitigation and invest in policies that protect the environment and safeguard public health.
Conclusion
The 2025 wildfire season in Canada is a stark reminder of the growing threat posed by climate change. The fires are not only destroying vast tracts of land but also endangering public health on both sides of the border. With climate change exacerbating the intensity of these fires, it is clear that more needs to be done to prevent future disasters. By improving forest management, investing in firefighting resources, and addressing climate change, Canada and the world can work towards reducing the devastating impact of wildfires and protecting communities from their harmful effects.
As the global community continues to grapple with the realities of climate change, Canada’s wildfire crisis serves as a critical call to action for a unified, long-term response to safeguard both the environment and public health.
For more travel news like this, keep reading Global Travel Wire