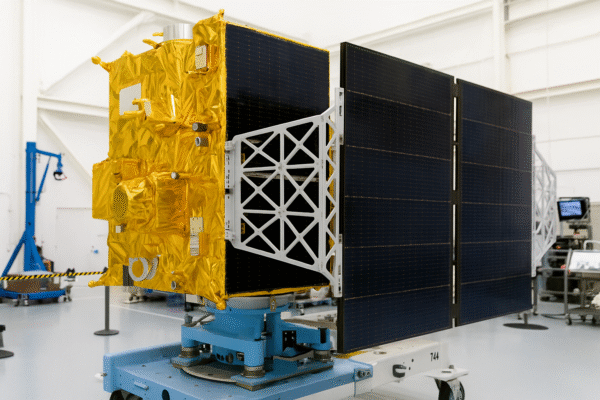
Boeing has taken a major step forward in aerospace innovation with the introduction of 3D-printed solar arrays for satellites, marking a turning point for both satellite deployment and the development of space tourism infrastructure. This breakthrough reduces production time by up to 50 percent, accelerating the timeline for launching satellites into orbit. The first units will fly with Spectrolab solar cells aboard small satellites from Millennium Space Systems, further demonstrating Boeing’s commitment to advancing sustainable and efficient space technologies.
By integrating additive manufacturing into satellite production, Boeing is transforming the way solar arrays are designed and built. Instead of relying on numerous individual components, the new system allows for complex features such as harness paths and attachment points to be directly printed into the panels. This reduces assembly time, improves efficiency, and ensures greater durability for long-term use in space.
Why This Matters for Satellites and Space Tourism
The introduction of 3D-printed solar arrays has immediate implications for the rapid growth of the satellite industry. Satellites are vital for communications, navigation, weather monitoring, and scientific exploration—but they are also increasingly critical for space tourism infrastructure.
As the global space tourism sector expands, satellites will provide essential support for:
- Internet connectivity for passengers and orbiting facilities.
- Navigation and safety systems required for spacecraft operations.
- Data transmission for both tourists and ground-based support teams.
By cutting production times and lowering costs, Boeing’s technology ensures satellites can be deployed more quickly and in greater numbers. This is particularly significant for the creation of low-Earth orbit constellations, which will form the digital backbone of future tourism ventures beyond Earth.
From Manufacturing to Orbit: Speeding Up Deployment
One of the biggest challenges in satellite development has traditionally been time-intensive assembly and testing. With 3D printing, Boeing addresses this challenge head-on. The new arrays, made from proven flight materials, are lighter, more durable, and easier to reproduce at scale.
The streamlined design process also means fewer parts, reducing the risk of malfunctions in orbit. For the space tourism industry, reliability is critical—whether supporting a passenger spacecraft, an orbital hotel, or a lunar tourism mission. Faster deployment ensures that infrastructure will be ready to meet the demands of an emerging market projected to grow dramatically in the coming decade.
Boeing’s Role in Shaping the Future of Space Tourism
Boeing has long been at the forefront of aerospace advancements, from commercial aviation to space exploration. With this latest development, the company is also playing a pioneering role in space tourism.
By improving the efficiency of satellite technology, Boeing provides the backbone for many of the services space tourists will rely on, including:
- Global high-speed internet while traveling in orbit.
- Satellite communications for secure links between Earth and spacecraft.
- Energy supply systems to power emerging space habitats and tourism stations.
This move also aligns with a wider industry shift toward sustainable space exploration. Additive manufacturing reduces waste, lowers costs, and enables rapid innovation, ensuring that space tourism infrastructure can expand responsibly and efficiently.
A Growing Market for Space-Based Travel
Industry forecasts indicate that the space tourism market could exceed billions of dollars in annual revenue by the 2030s, with companies exploring orbital flights, lunar missions, and even Mars exploration. Boeing’s technology plays a crucial role in enabling these ambitions by ensuring satellites can be produced quickly enough to support the sector’s rapid evolution.
For example, future orbital hotels will rely on robust satellite systems for communications, navigation, and passenger services. Similarly, tourism missions to the Moon will require high-capacity satellites to manage navigation, communication, and emergency support.
As infrastructure expands, space tourism could evolve from a niche luxury experience into a broader commercial sector, making travel beyond Earth more affordable and accessible.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While Boeing’s 3D-printed solar arrays represent a breakthrough, challenges remain in scaling the technology and integrating it into broader aerospace infrastructure. The industry will need to:
- Continue investing in testing and validation of 3D-printed space components.
- Ensure satellites meet international safety and regulatory standards.
- Balance the push for rapid expansion with sustainability and space debris management.
However, these challenges are also opportunities. By leading the way in innovation, Boeing can strengthen its role as a key enabler of global space tourism. Its advances in additive manufacturing not only speed up satellite deployment but also pave the way for more resilient, cost-effective space infrastructure.
Looking to the Future: A Connected Space Tourism Economy
The broader vision for Boeing’s innovation goes beyond satellites—it is about creating a connected space tourism economy. Faster satellite deployment will enable:
- Orbital broadband networks supporting spacecraft, stations, and future lunar bases.
- Real-time communications between tourists and ground crews.
- Data-driven services such as live streaming from orbit or lunar tourism experiences.
As satellites become cheaper and faster to produce, the possibility of building dedicated networks for space tourists becomes realistic. This connectivity will be vital for creating safe, enjoyable, and sustainable travel experiences.
Conclusion: Boeing’s Bold Step Toward the Future
Boeing’s introduction of 3D-printed solar arrays is more than an aerospace breakthrough—it is a strategic step toward the future of space tourism. By reducing production times and enabling faster satellite deployment, Boeing is laying the groundwork for the infrastructure that will support human travel beyond Earth.
As space tourism shifts from science fiction to reality, innovations like these will ensure that travelers can enjoy safe, connected, and sustainable journeys. Boeing’s commitment to additive manufacturing and aerospace leadership positions it at the heart of this transformation, bridging the gap between advanced technology and the new frontier of global tourism.
With satellites powering everything from communications to navigation, Boeing’s leap forward ensures that the dream of space tourism is not only possible but increasingly within reach.
For more travel news like this, keep reading Global Travel Wire